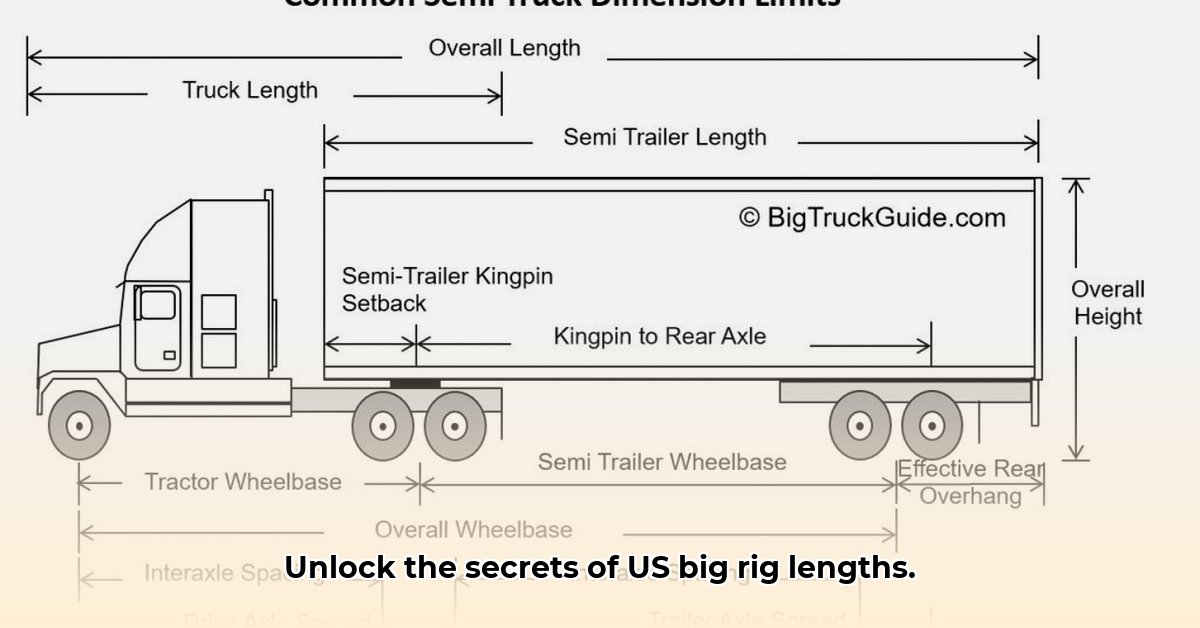
Understanding US tractor-trailer length regulations is crucial for efficient and legal trucking operations. Federal guidelines provide a base, but significant state-level variations create complexities. This guide clarifies these rules, offering actionable steps to navigate this challenging landscape. Are you ready to master the maze of state-specific regulations? For more on truck dimensions, see tractor trailer height.
Length of Tractor-Trailer: Navigating the US Trucking Maze
Federal regulations largely standardize width (8.5 feet) and height (13.5 feet) for tractor-trailers, primarily due to bridge clearances. However, length regulations vary significantly by state, impacting routing, costs, and equipment choices. This inconsistency presents a major challenge for trucking companies operating nationwide. What are the most significant implications of these inconsistencies?
Federal Rules: A Foundation with State-Level Variations
While federal regulations establish minimum lengths for certain configurations, maximum lengths are determined at the state level. This inconsistency creates a complex regulatory environment for trucking operations. How can trucking companies better manage the complexities of state-level variations?
State-by-State Differences: A Complex Regulatory Landscape
Each state independently sets its maximum tractor-trailer length. Some states, such as Texas and Oklahoma, permit longer combinations (up to 59 feet), while others enforce a 53-foot limit. This variability directly impacts logistical planning, operational costs, and equipment selection for trucking businesses. What strategic approaches can mitigate the challenges posed by inconsistent state regulations?
The Impact on Trucking Operations: Real-World Challenges
Inconsistent length regulations lead to several operational challenges:
Route Planning Complexity: Determining optimal routes requires meticulous state-by-state assessments of length restrictions. This adds significant time and administrative overhead.
Increased Operational Costs: Increased planning and potential delays translate directly into higher fuel consumption, driver labor costs, and administrative expenses.
Limited Equipment Choices: The need to comply with varying state regulations often necessitates a diverse fleet of trailers, increasing capital investment and maintenance costs.
Risk of Non-Compliance: Staying abreast of constantly evolving state-specific rules is paramount to avoid costly fines and legal repercussions. What strategies can mitigate these risks and ensure compliance?
Strategies for Success: Optimizing Operations in a Complex Regulatory Landscape
Effective strategies for navigating these challenges include:
Investing in Advanced Route Planning Software: Sophisticated software can significantly streamline route planning by considering real-time length limitations and traffic conditions, leading to enhanced efficiency.
Maintaining a Diverse Trailer Fleet: Possessing a variety of trailers to accommodate different state regulations ensures operational flexibility.
Advocating for National Standardization: Collaboration and advocacy efforts to promote uniform national standards would simplify operations across the board.
Continuous Monitoring of Regulatory Updates: Staying informed on changes to state regulations is crucial for maintaining compliance. What resources are available to track regulatory changes effectively?
Understanding the Risks and Implementing Mitigation Strategies
The following table summarizes the risks associated with inconsistent length regulations and corresponding mitigation strategies:
| Risk Factor | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breaking Length Limits | High | Very High | Utilize advanced route planning software, provide comprehensive driver training. |
| Increased Costs | High | High | Implement optimization strategies like fuel-efficient routing and efficient fleet management. |
| Complex Route Planning | High | Medium | Leverage advanced route-planning software and tools. |
| Accidents from Overlength Trailers | Low | Very High | Enforce strict adherence to regulations and invest heavily in driver training. |
This table highlights the significant risks associated with inconsistent state regulations. Proactive risk management strategies are critical for success in the US trucking industry.
Obtaining Oversized Load Permits: A State-by-State Guide
While federal regulations set baseline weight restrictions (typically 80,000 lbs gross vehicle weight), states independently regulate oversized load permits. Each state's permitting process, criteria, and timelines differ significantly. What is the most efficient approach for obtaining state-specific oversized load permits?
Navigating State-Specific Regulations: A Step-by-Step Approach
Securing oversized load permits involves a multi-step process:
Detailed Route Planning: Accurately map your route, noting every state traversed, as regulations vary drastically.
Thorough Research of State Regulations: Consult each state's Department of Transportation (DOT) website to determine specific dimensions, weight limits, and prohibited routes.
Gather Essential Documentation: Compile necessary paperwork such as dimension certificates, insurance information, detailed route plans, and engineering reports if necessary.
Submit Applications: Submit applications via the designated state channels (online portals or traditional methods). Allow ample processing time.
Arrange for Escorts (if required): Many states mandate escort vehicles for oversized loads.
Plan for Potential Delays: Incorporate buffer time to account for permit processing delays and unexpected complications.
Key Considerations for Oversized Loads: Beyond Weight and Dimensions
Permitting considerations extend beyond weight and include:
- Dimensions: Height, width, and length all significantly impact permit requirements.
- Route Restrictions: Bridges, tunnels, and certain roads may be off-limits to oversized loads.
- Time-of-Day Restrictions: Some areas limit oversized load movement to specific hours.
- Seasonal Bans: Weather conditions may necessitate temporary bans.
Mitigating Risks Associated with Oversized Loads
Minimizing risks associated with oversized loads requires a multifaceted approach:
- Professional Assistance: Consider utilizing experienced third-party permit procurement services.
- Thorough Planning: Invest significant time and resources into route planning and contingency plans.
- Specialized Driver Training: Train drivers on proper handling of oversized loads and navigating complex routes.
The information provided serves as a general guide. Always consult the official website of each state's Department of Transportation for the most accurate and up-to-date information. Staying informed is paramount to successful, legal, and efficient trucking operations.